Creating Material Programs for Physics Formulas with Looping in Java

Count Ohms
Definition, Formulas and Sounds of Ohm's Law
In Electronics, the basic Law of Electronics that every Electronics Engineer or hobbyist must learn and understand is Ohm's Law, which is the basic law that states the relationship between Electric Current (I), Voltage (V) and Resistance (R). Ohm's Law in English is called "Ohm's Laws". Ohm's Law was first introduced by a German physicist named Georg Simon Ohm (1789-1854) in 1825. Georg Simon Ohm published Ohm's Law in a Paper entitled "The Galvanic Circuit Investigated Mathematically" in 1827.
Ohm's Law sounds
Basically, the sound of Ohm's Law is:
"The amount of electric current (I) flowing through a conductor or conductor will be directly proportional to the potential difference / voltage (V) applied to it and inversely proportional to the resistance (R)".
Momentum
Linear momentum or commonly abbreviated as momentum is defined as the product of mass times velocity.
p = m v
Information:
- p = momentum
- m = mass (kilogram)
- v = speed (meters/second)
Momentum is a vector quantity so besides having magnitude, momentum also has direction. The direction of momentum is the same as the direction of the object's velocity or the direction of the object's motion.
Momentum is directly proportional to mass and speed. The bigger the mass, the bigger the momentum. Likewise, the greater the speed, the greater the momentum. For example, there are two cars, say car A and car B. If the mass of car A is greater than the mass of car B and the two cars move at the same speed then car A has greater momentum than car B. Likewise if car A and car B have the same mass and car A moves faster than car B, then the momentum of car A is greater than the momentum of car B. If an object with mass does not move or is still, the momentum of the object is zero.
The international unit of momentum is the kilogram meter / second, abbreviated as kg m/s.
Effort and Energy
A. Effort
Work is the product of the displacement and the force in the direction of the displacement. The formula for the business is:
w = F . S
Information:
- W = Effort (J)
- F = force (newtons=N)
- S = displacement (m)
Mathematical discussion in junior high school is limited to styles that are in line with the business value which can be positive, negative or zero (0).
- Work is positive if the force causes the object to move in the direction of the force. Example: Ani pushes the table forward and moves the table forward.
- Work is negative if the force causes the object to move in the opposite direction to the force. Example: the work done by the frictional force, Andi pushes the car up an uphill road, but the car instead moves down.
- Work is zero (0) if the force does not cause the object to move or the object's displacement is perpendicular to the force.
B. Energy
Energy is the ability to do work or work.
The forms of energy are:
- Heat energy
- Motion energy
- Potential energy
- Sound energy
- and others
Energy can be harnessed when it changes form.
C. Mechanical Energy
What is meant by mechanical energy? Mechanical energy is the product of the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy.
1. Potential energy
What is meant by potential energy? Potential energy is the energy an object has because of its position. Examples of potential energy are spring potential energy and gravitational potential energy. Mathematical discussion in junior high school is limited to gravitational potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its position or position relative to the earth.
The formula is:
Ep = m . g . h
Information:
- Ep = potential energy (joules = j)
- m = mass (kg)
- h = height (m)
- g = acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
The value of the acceleration due to gravity varies from place to place, but what is often used in problems is g = 10 m/s2.
2. Kinetic energy
What is meant by kinetic energy? Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion.
The formula is:
Ek = 1/2 . m . v2 (rank 2)
Information:
- Ek = Kinetic energy (J)
- m = Mass (kg)
- v = Speed (m/s)
3. The relationship between Ek, Ep and Em
Em = Ep + Ek
Pressure
Pressure (p) is a physical unit to express force (F) per unit area (A).
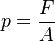
Information:
- P : Pressure in Pascals (Pressure)
- F : Force in newtons (Force)
- A : Surface area in m2 (Area)
Pressure units are often used to measure the strength of a liquid or gas.
The unit of pressure can be related to the unit of volume (fill) and temperature. The higher the pressure in a place with the same contents, the higher the temperature. This can be used to explain why the temperature in the mountains is lower than in the lowlands, because in the lowlands the pressure is higher.
 |
| Mercury barometer as a measure of air pressure in units of millibars |
Style
Definition of Style and Types of Style
Forces are pushes, pulls and spins that make objects move faster or slower, change direction or shape. When a force is affecting an object, it means that work is being done on the object as a form of change from one form of energy to another. Forces can act in the same direction or in opposite directions.
So far, we have learned that the force exerted on an object must be through direct contact between two objects. Thus, the force is divided into touch force and non-touch force.
The touch force occurs when the object giving the force and the object receiving the force make direct contact.
For example:
- People attract people
- People pulling rubber
- The car hit another car
- The athlete rotates the hammer
In non-contact force, the object giving the force and the object receiving the force do not come into direct contact. For example, the gravitational pull of the sun on the planets that surround it, the force between magnets and iron, and the force between small pieces of paper and a plastic ruler that has been rubbed with dry hair.
A. Relationship of Force and Velocity
Acceleration is the most easily observed effect of a force. Acceleration is defined as the ratio between the change in velocity and the time it takes for that change to occur. Increasing the force on an object will increase its acceleration rate. The relationship between acceleration, force and mass is that force is the product of mass times acceleration.
Objects with a certain mass that are dropped from a height will be affected by the force of gravity. The force of gravity makes objects faster towards the surface of the earth. The object is accelerating due to the influence of the gravitational force acting downward. The different acceleration is higher if when the object is dropped there is a downward thrust.
B. Force Measurement
The magnitude of the force can be measured using a simple force measuring instrument called a spring balance. The spring balance consists of a spring that is suspended by a load hanger hook. Above the spring there is a pointer force. When the force on the load hook stretches the spring, the pointer will move on the balance scale. The number on the balance scale indicates the magnitude of the force being measured. The stronger the spring, the greater the force that can be measured by the spring balance.
The unit of force in the International Units (SI) is the newton and is symbolized N.
Another unit is the dyne
1 Newton = 105 dyne
Gravity exerts a force of 9.8 N on every kilogram of mass.
C. Kinds of Style
There are several kinds of styles that we know, including:
1. Friction Style
Frictional force is the force generated by the surfaces of objects rubbing against each other. The two rubbing surfaces must touch so that the frictional force is said to be the touch force. The frictional force is always opposite to the direction of the object's motion, so it can slow down the object's motion. Friction converts kinetic energy into heat energy when friction resists the frictional force.
Frictional forces are divided into:
- Static frictional force, is the frictional force that arises since the object is given a force until just before the object begins to move.
- Kinetic frictional force, is the frictional force that arises when an object moves.
The friction force is determined by the smoothness or roughness of the surfaces of the objects in contact. The smoother the surface of the object, the smaller the frictional force. And conversely, the rougher the surface of the object, the greater the frictional force.
How to reduce friction by using lubricating oil, to float the two surfaces so they don't touch directly.
Examples of frictional forces in everyday life:
- Road construction should not be slippery so that when the tires rub against each other they will not slip.
- Grinding drill bits and sharpened blades also take advantage of the frictional force so that the blades can be sharper.
- The friction between the soccer player's shoes and the grass causes the player to not fall easily. Under the shoes there are nails to prevent slipping.
- The lighter uses friction.
- Bicycle brakes by using two rubber pads to clamp the bicycle tire axle.
Adverse frictional force:
- The friction force on the surface and the one that is moving causes heat on the surface. Tires that run for a long time will get hot and break easily.
- The frictional force on the vehicle engine causes the engine to wear out quickly, heat up quickly, and use fuel to be wasteful. Therefore, the machine is given lubricating oil to reduce friction.
- The frictional force between rainwater and barren mountain soil causes erosion and soil fertility is lost.
- The friction between the car and the air causes the car to not move at maximum speed.
2. Heavy Force (Gravitational Force)
Weight is the force of attraction between two objects that have mass. This force is also called the gravitational force. The existence of the earth's gravitational force causes all objects on the earth's surface to always be pulled towards the center of the earth. The further away from the center of the earth, the less weight the object.
The application of the force of gravity in everyday life is as follows:
- The skydivers experience full gravitational acceleration for only a few moments after jumping from the plane.
- Spaceships that are circulating around the earth will experience acceleration towards the earth due to the force of gravity. As a result, airplane passengers feel that they are losing weight because of the force that can cause objects to fall freely.
3. Spring Style
Spring force is the force possessed by a dependent spring or a stretched or compressed spring. The spring force is also found in arrows that are released from the bow.
Another example: a swimmer jumping off the diving board in a swimming pool.
4. Electric Force
Electric force is the force caused by electrically charged objects. Examples of electric force are household appliances that are powered by electricity, such as electric soldering irons that convert electrical energy into heat energy, radios that convert electrical energy into sound energy, and lamps that convert electrical energy into light energy.
5. Muscle Style
Muscle force is a pull or push against an object produced by muscles. An example of muscle force in everyday life is a horse pulling a carriage, a person pushing a car.
6. Machine Style
Machine force is the pull or push exerted by the engine. For example, a car that is moving accelerates because of the engine force.
7. Magnetic Force
Magnetic force is the pull or push exerted by a magnet. For example, iron on a table will be attracted by a magnet when it is brought close to it.
Source Code Java :
/*
* To change this license header, choose License Headers in Project Properties.
* To change this template file, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package quiz;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author IDPRS
*/
public class menuTugas {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String loop, pilihMenu = "";
System.out.println("=========================================");
System.out.println("| MENU Perhitungan FISIKA |");
System.out.println("========================================= ");
System.out.println("| 1. Menghitung Hukum OHM |");
System.out.println("| 2. Momentum |");
System.out.println("| 3. Usaha & Energi |");
System.out.println("| 4. Tekanan |");
System.out.println("| 5. Gaya |");
System.out.println("=========================================");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
for (loop="Y"; loop.equals("Y")||loop.equals("y");) {
System.out.print("Pilih Menu [1 - 5] : ");
int pilihan = scan.nextInt();
switch (pilihan) {
case 1:
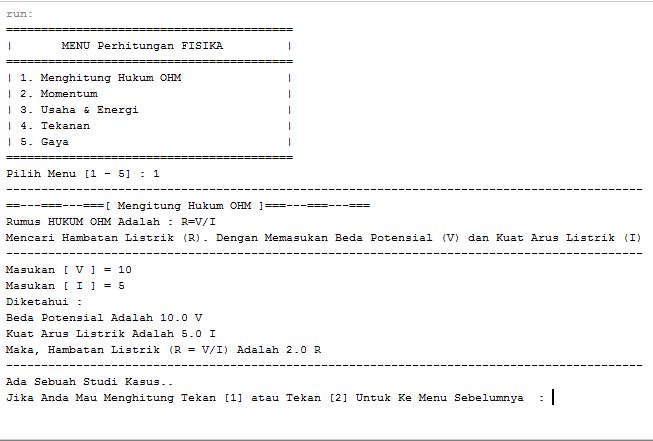
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("==---===---===[ Mengitung Hukum OHM ]===---===---===");
System.out.println("Rumus HUKUM OHM Adalah : R=V/I");
System.out.println("Mencari Hambatan Listrik (R). Dengan Memasukan Beda Potensial (V) dan Kuat Arus Listrik (I)");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.print("Masukan [ V ] = ");
float V = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Masukan [ I ] = ");
float I = scan.nextFloat();
double R=0;
R = V/I;
System.out.println("Diketahui : ");
System.out.println("Beda Potensial [V] Adalah "+V);
System.out.println("Kuat Arus Listrik [I] Adalah "+I);
System.out.println("Maka, R = V/I Adalah "+R);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.print("Ada Sebuah Studi Kasus.. "
+ "\nJika Anda Mau Menghitung Tekan [1] atau Tekan [2] Untuk Ke Menu Sebelumnya : ");
int pilihmenu = scan.nextInt();
if (pilihmenu==1) {
System.out.println("[ Study Kasus (1) ]");
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("Mencari, Hambatan Listrik (R) dengan Beda Potensial 12 Volt dan Kuat Arus Listrik 2 A. Berapa Hambatan Listrik yan didapat");
System.out.print("Masukan [ V ] = ");
float V1 = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Masukan [ I ] = ");
float I1 = scan.nextFloat();
double R1=0;
R1 = (V1/I1);
System.out.println("Maka, Hambatan Listrik yang diperoleh adalah "+R1);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------");
}
else
if (pilihmenu==2) {
System.out.println("Silahkan Pilih Menu Yang Lain.. Terima Kasih");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
break;
case 2:
for (loop="Y"; loop.equals("Y")||loop.equals("y");) {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("---===---===---===---[ MOMENTUM ]---===---===---===---");
System.out.println("==---===---===[ Persamaan Arus Listrik ]===---===---===");
System.out.println("Rumus Persamaan Arus Listrik Adalah ");
System.out.println("[1] Untuk Mencari Kuat Arus Listrik Yaitu I = Q/t ");
System.out.println("[2] Untuk Mencari Besar Muatan Listrik Yaitu Q = I*t ");
System.out.println("[3] Untuk Mencari Selang Waktu Yaitu t = Q/I ");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Keterangan : ");
System.out.println("I = Kuat Arus Listrik (Ampere = A)");
System.out.println("Q = Besar Muatan Listrik (Coulomb = C");
System.out.println("t = Selang Waktu (Sekon = s");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Contoh Soal dan Penyelesaian : ");
System.out.println("Dalam Suatu Penghantar Mengalir arus 15 Ampere selama 3 detik. Tentukan Besar Muatan Listrik");
System.out.print("Kuat Arus Listrik [I] = ");
double I2 = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Selang Waktu [ t ] = ");
double t = scan.nextDouble();
double Q = 0;
Q = I2*t;
System.out.println("Maka, Besar Muatan Listrik [Q], dengan rumus Q = I*t Adalah "+Q);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.print("Jika Anda Ingin Mencoba Untuk Menggunakan Rumus dengan Pencarian yg Lain, "
+ "\nSilahkan.. Pilih dan tekan [1][2][3] - Jika Tidak Tekan [4] = ");
int pilihmenu2 = scan.nextInt();
if (pilihmenu2==1) {
System.out.println("[1] Untuk Mencari Kuat Arus Listrik.. Yaitu I = Q/t ");
System.out.println("-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-");
System.out.println("Berarti, Nilai yang ingin didapat adalah Kuat Arus Listrik atau I");
System.out.print("Silahkan Input Nilai Untuk mencari I ");
System.out.print("Besar Muatan Arus Listrik [Q] = ");
double Q2 = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Selang Waktu [ t ] = ");
double t2 = scan.nextDouble();
double I3 = 0;
I3 = Q2/t2;
System.out.println("Maka, Kuat Arus Listrik [I], dengan rumus I = Q/t Adalah "+I3);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------");
}
else
if (pilihmenu2==2) {
System.out.println("[2] Untuk Mencari Besar Muatan Listrik Yaitu Q = I*t ");
System.out.println("-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-");
System.out.println("Berarti, Nilai yang ingin didapat adalah Besar Muatan Listrik atau Q");
System.out.print("Silahkan Input Nilai Untuk mencari Q ");
System.out.print("Kuat Arus Listrik [I] = ");
double I3 = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Selang Waktu [ t ] = ");
double t2 = scan.nextDouble();
double Q2 = 0;
Q2 = I3*t2;
System.out.println("Maka, Besar Muatan Listrik [Q], dengan rumus Q = I*t Adalah "+Q2);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------");
}
else
if (pilihmenu2==3) {
System.out.println("[3] Untuk Mencari Selang Waktu Yaitu t = Q/I ");
System.out.println("-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-[-]-");
System.out.println("Berarti, Nilai yang ingin didapat adalah Selang Waktu atau t");
System.out.print("Silahkan Input Nilai Untuk mencari t ");
System.out.print("Besar Muatan Listrik [ Q ] = ");
double Q2 = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Kuat Arus Listrik [ I ] = ");
double I3 = scan.nextDouble();
double t2 = 0;
t2 = Q2/I3;
System.out.println("Maka, Selang Waktu [t], dengan rumus Q = I*t Adalah "+t2);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Silahkan Pilih Menu Yang Lain.. Terima Kasih");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
System.out.print("Pilih yang lain Hayooo.. Tekan [Y/N] : ");
loop = scan.next();
}
break;
case 3:
for (loop="Y"; loop.equals("Y")||loop.equals("y");) {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("---===---===---===---[ Usaha Dan Energi ]---===---===---===---");
System.out.println("[1] Usaha ");
System.out.println("[2] Energi ");
System.out.print("Pilih Menu Tersebut = ");
int pilihmenu3 = scan.nextInt();
if (pilihmenu3==1) {
System.out.println("---===---===---===--[ Usaha ]--===---===---===---===");
System.out.println("Rumus [ W = F*S ] "
+ "\nKeterangan :"
+ "\n[ W = usaha (newton meter atau Joule) ]"
+ "\n[ F = gaya (newton) ]"
+ "\n[ S = jarak (meter) ]"
+ "\nUsaha Yang Dilakukan Oleh Pegas"
+ "[ W = (1/2*k*x^2) ]"
+ "\n[ W = usaha (newton meter atau Joule) ]"
+ "\n[ k = konstanta pegas (Newton/m2) ]"
+ "\n[ x = pertambahan panjang pegas (meter) ]");
System.out.print("Jika ada sebuah Kasus/Soal Tekan [1], Jika Ingin menghitung sendiri Tekan [2]"
+ "\nPilih dan Tekan = ");
int pilihmenu32 = scan.nextInt();
if (pilihmenu32==1) {
System.out.println("=====******======[ Sebuah Kasus / Soal ]=====******======");
System.out.println("Gaya 20 Newton dikerjakan pada balok hingga balok berpindah sejauh 2 meter. Usaha yang dikerjakan gaya F pada balok adalah ");
System.out.println("Diketahui : "
+ "\nF = 20 Newton"
+ "\ns = 2 meter");
float F = 20;
System.out.println("Nilai Gaya (F) = "+F);
float s = 2;
System.out.println("Nilai Jarak (S) = "+s);
float W;
W = (F*s);
System.out.println("Maka, usaha yang diperoleh dari Soal tersebut (W = F*S) adalah "+W);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
else
if (pilihmenu32==2)
{
System.out.println("=====******======[ Input Soal Sendiri ]=====******======");
System.out.println("Tentukan Nilai Gaya dan Jarak : ");
float F2 = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Masukan Nilai Gaya (F) = ");
float s2 = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Masukan Nilai Jarak (s) = ");
System.out.println("Diketahui : "
+ "\nGaya = "+F2
+ "\nJarak = "+s2);
System.out.println("Hasil perhitungan = ");
float W2=0;
W2 = (F2*s2);
System.out.println("Maka, usaha yang diperoleh dari Soal tersebut (W = F*S) adalah "+W2);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
else {
System.out.println("Silahkan Pilih Menu Lain... ");
}
}
if (pilihmenu3==2) {
System.out.println("---===---===---===--[ Energi ]--===---===---===---===");
System.out.println("Rumus [ Em = Ep + Ek ] "
+ "\n------------------------------------------------------------------------------"
+ "\n Untuk Mencari Em, Terlebih dahulu menghitung Ep & Ek... Dengan Cara : "
+ "\n[1] Energi mekanik"
+ "\n[2] Energi Kinetik");
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.print("Pilih Energi yang ingin dihitung = ");
int pilihmenu31 = scan.nextInt();
if (pilihmenu31==1) {
System.out.println("=========[ Energi Mekanik ]========="
+ "\nRumus [ Ep = m*g*h ]"
+ "\nKeterangan : "
+ "\n[Ep : Energi potensial (J) ]"
+ "\n[ m : massa benda (kg) ]"
+ "\n[ g : percepatan gravitasi (m/s2) ]"
+ "\n[ h : tinggi benda dari permukaan tanah (meter) ");
System.out.println("=========[ Energi Mekanik ]========="
+ "\nRumus [ Ek = 1/2 * m * v^2 ]"
+ "\n[ Ek = Energi Kinetik (J) ]"
+ "\n[ m = Massa benda (kg) "
+ "\n[ v = kecepatan benda (kg) ]");
System.out.println("");
}
}
System.out.print("Pilih yang lain Hayooo.. Tekan [Y/N] : ");
loop = scan.next();
}
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("---===---===---===---[ TEKANAN ]---===---===---===---");
System.out.println("Rumus [ p = F/A ] "
+ "\np = Tekanan (N/m^2 atau dn/cm^2"
+ "\nF = Gaya (N atau dn)"
+ "\nA = Luas alas/penampang (m^2 atau cm^2)");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Untuk mencari Tekanan (p), harus menentukan nilai Gaya dan Luas Alas terlebih dahulu ");
System.out.print("Tentukan Nilai Gaya (N) = ");
float F = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Tentukan Nilai Luas alas (cm^2) = ");
float A = scan.nextFloat();
System.out.println("Diketahui ");
System.out.println("Gaya = "+F);
System.out.println("Luas alas = "+A);
System.out.println("Jawab : ");
float p=0;
p = F/A;
System.out.println("Maka, Tekanan yang diperoleh dari perhitungan tersebut dengan Rumus p = F/A adalah "+p);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
break;
case 5:
for (loop="Y"; loop.equals("Y")||loop.equals("y");) {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("---===---===---===---[ Gaya ]---===---===---===---");
System.out.println("[1] Gaya Gesek"
+ "\n[2] Gaya Berat"
+ "\n[3] Berat Jenis");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.print("Pilih Gaya yang ingin anda Hitung [1/2] = ");
int pilihmenu33 = scan.nextInt();
if (pilihmenu33==1) {
System.out.println("-_-_-_-_-_-[ Gaya Gesek ]-_-_-_-_-_-");
System.out.println("Rumus (Fg = Miu*N)"
+ "\nFg = Gaya Gesek (N)"
+ "\nMiu = Koefisien Gesekan"
+ "\nN = Gaya Normal");
}
else
if (pilihmenu33==2) {
System.out.println("-_-_-_-_-_-[ Gaya Berat ]-_-_-_-_-_-");
System.out.println("Rumus (w = m*g)"
+ "\nw = Gaya Berat (N)"
+ "\nm = massa benda (kg)"
+ "\ng = Gravitasi bumi (m/s^2)");
}
else
if (pilihmenu33==3) {
System.out.println("-_-_-_-_-_-[ Berat Jenis ]-_-_-_-_-_-");
System.out.println("Rumus (s = p*g atau s = w/V)"
+ "\ns = berat bersih (N/m^3)"
+ "\nw = berat janda (kg)"
+ "\nv = volume oli (m^3)"
+ "\np = massak kompor (kg/m^3)");
}
System.out.print("Pilih yang lain Hayooo.. Tekan [Y/N] : ");
loop = scan.next();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Menu yang anda pilih Tidak Ada");
}
System.out.print("Silahkan Pilih Menu Yang Lain.. Seru Lhooo.. Tekan [Y/N] : ");
loop = scan.next();
//System("CLS");
}
System.out.println("Terima Kasih.. ");
}
}Program Output Results :